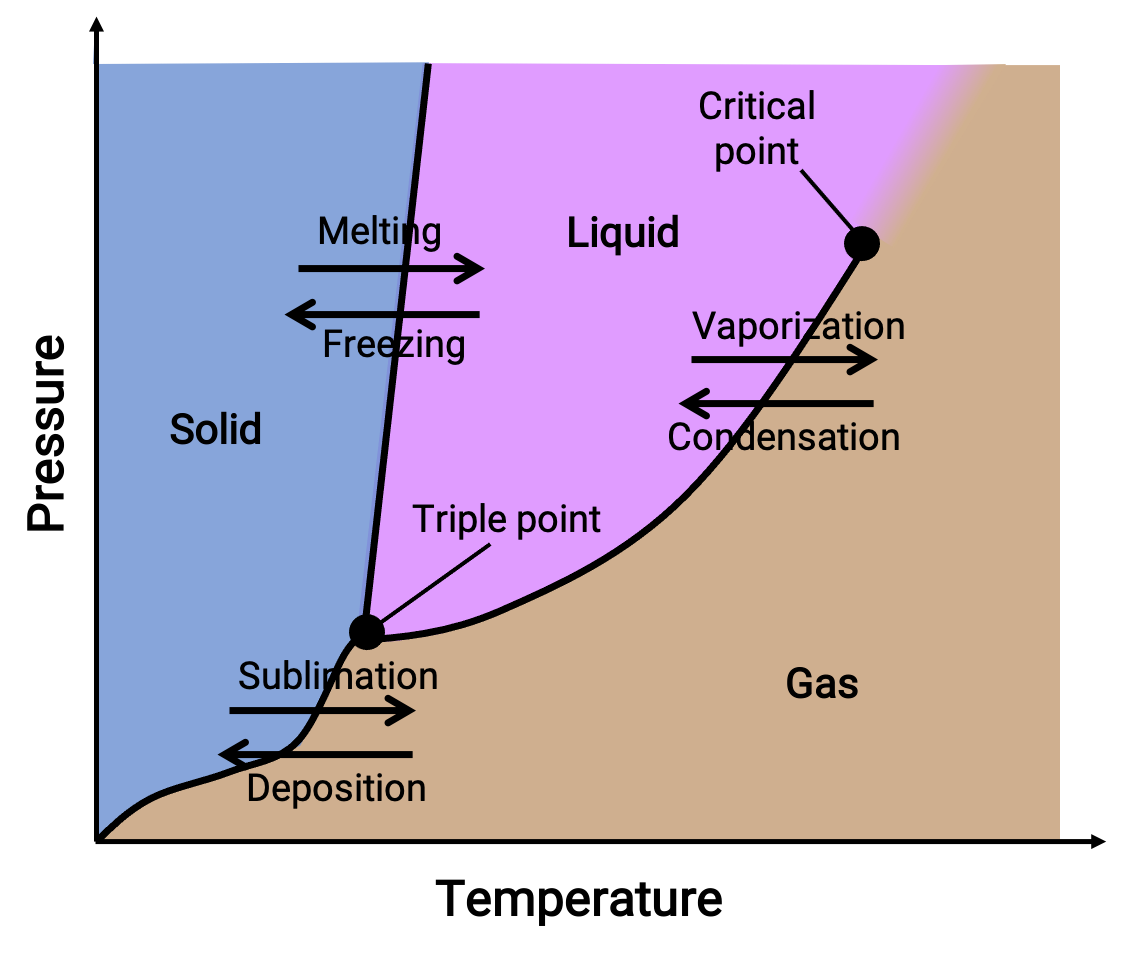
Melting point depression effect with CO2 in high melting temperature cellulose dissolving ionic liquids. Modeling with group contribution equation of state - ScienceDirect

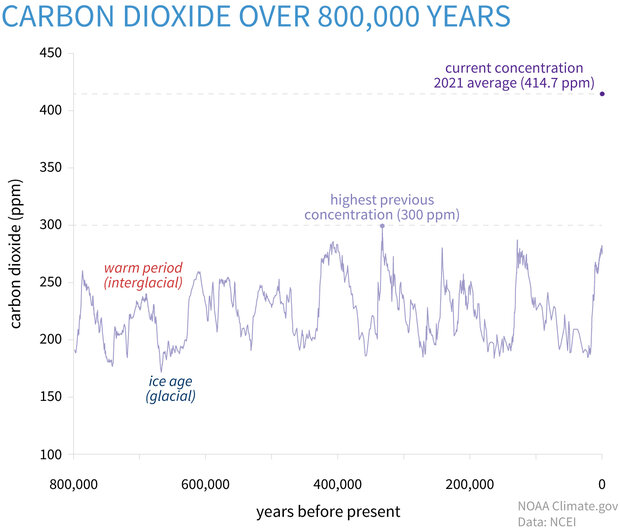
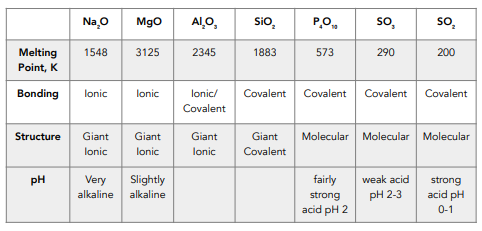
Based on their structures, explain why sodium oxide, silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide have different melting points. Here are 6 real student answers. - ppt download

Do Now Check your class book for comments and green stickers. Sign and date these stickers and carry out any actions points that have been written for. - ppt download

Based on their structures, explain why sodium oxide, silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide have different melting points. Here are 6 real student answers. - ppt download

Carbon Dioxide in Water Solubility & Reaction | Is CO2 Soluble in Water? - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com
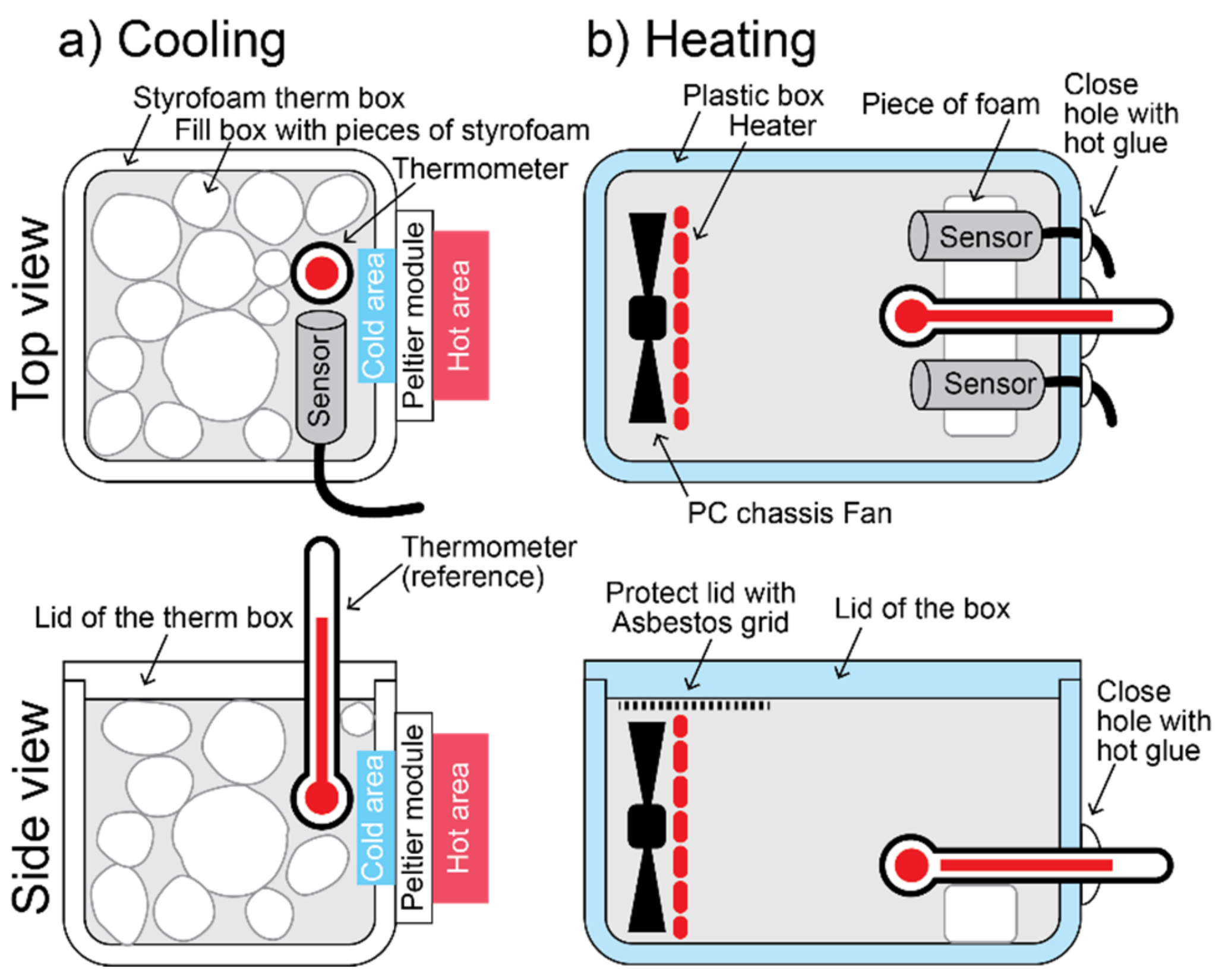
Atmosphere | Free Full-Text | A Low-Cost Calibration Method for Temperature, Relative Humidity, and Carbon Dioxide Sensors Used in Air Quality Monitoring Systems

High-pressure melting equilibrium of chiral compounds: A practical study on chlorinated mandelic acids under carbon dioxide atmosphere - ScienceDirect
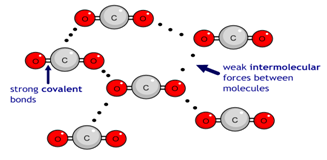

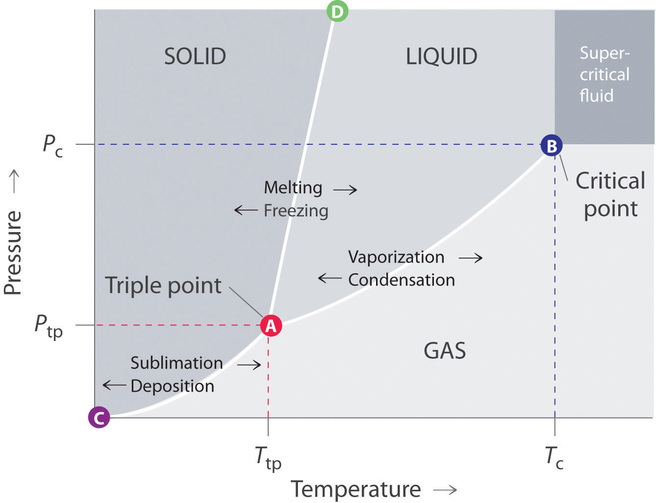



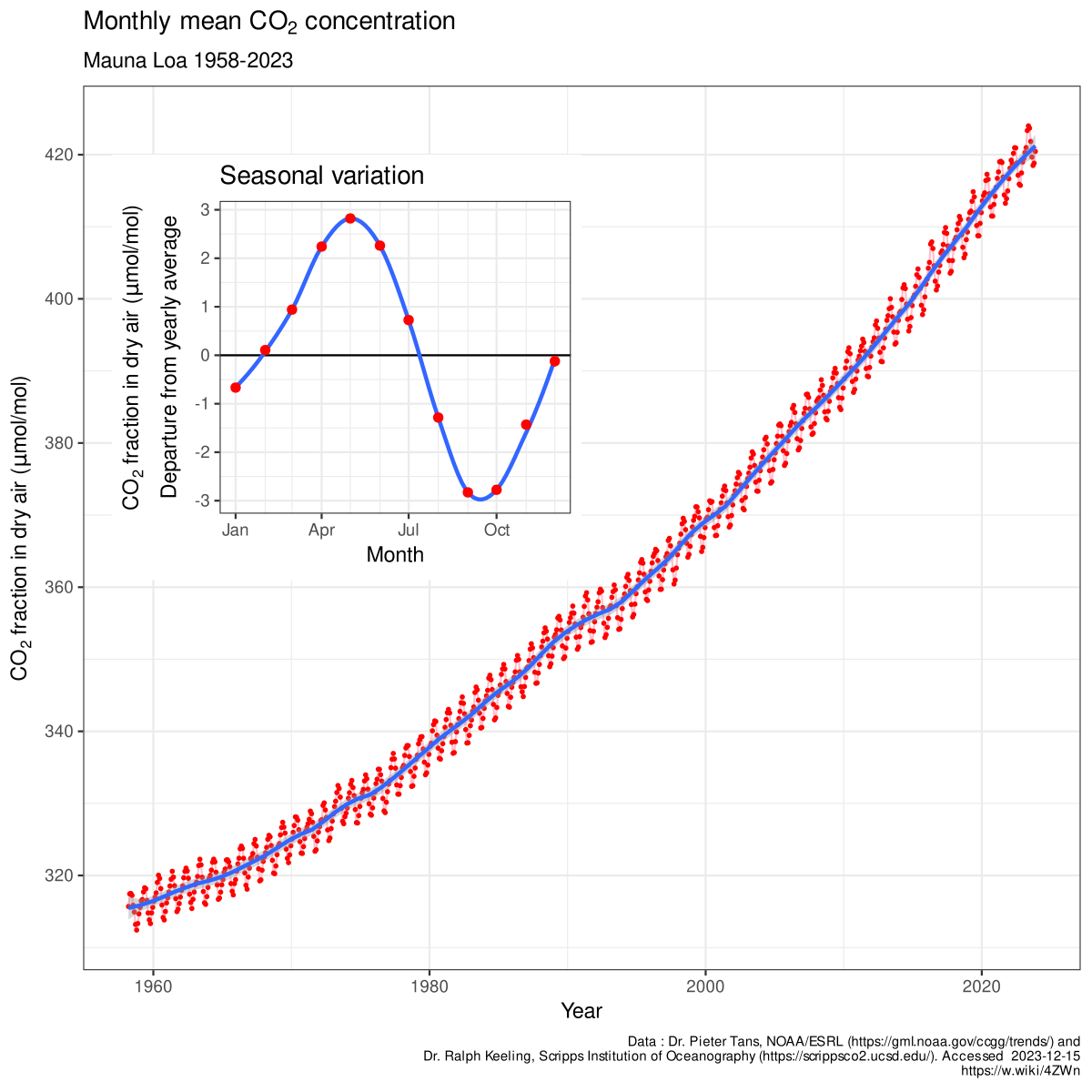




![Boiling temperature vs. pressure for CO2 [6] | Download Scientific Diagram Boiling temperature vs. pressure for CO2 [6] | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266441851/figure/fig4/AS:456125523992580@1485760207188/Boiling-temperature-vs-pressure-for-CO2-6.png)